一、背景
本文作为前文Router-based Federation的补充,顺带分析Observer状态的NameNode是如何分担读请求的。
我们所知HA架构中的HDFS使用Standby NameNode来作为Active NameNode的一个热备份,在故障转换时可以快速接管Client的请求。Standby NameNode与Active NameNode通过JournalNode来进行元数据的同步。所以Standby NameNode与Active NameNode是一摸一样的,因此Standby NameNode提供了一个绕开Active NameNode来读取数据的机会。通过Standby NameNode来读取数据会大大降低Active NameNode的压力并且也会极大的提升集群的吞吐。为了区分原有架构中Standby NameNode(不会提供读操作)对于能够提供读操作的Standby NameNode称之为Observer Node。
二、原理
在现有的HDFS架构中加入Observer节点,Observer节点通过JournalNode进行EditsLog的消费。然后客户端在获取到Active节点的TXID时将读请求发送到Observer节点来达到读写分流的目的,这样去减少Active NameNode的压力。
那么随之而来的就会有一个问题,读写一致性,即Active NameNode的元数据总是要相对领先的,Observer读取元数据必然会存在一定的延迟,所以对于一些新写入的数据Observer可能无法及时同步导致用户在读取新数据报错。
所以解决思路请参考另一篇文章,我觉得写的还可以Observer NameNode 的读写一致性保证。
三、客户端实现
思路:获取Active的State Id,并将Active的State Id携带到Observer进行元数据一致性的判断。
前文提到在RouterRpcClient中有一些invoke方法,社区方案对此进行了改造,在每个invoke方法中加入msync流程
boolean isObserverRead = nsObserverReadEnabled.getOrDefault(ns, observerReadEnabled)
&& isReadCall(m);
List<? extends FederationNamenodeContext> namenodes =
msync(ns, ugi, isObserverRead);
首先判断此Name Service是否开启了Observer可读功能,再判断远程调用的方法是否是处理读请求的方法(是否带@ReadOnly注解)。第二步msync方法来同步State Id,msync方法其中又分为两步:
final List<? extends FederationNamenodeContext> namenodes =
getNamenodesForNameservice(ns, isObserverRead);
此方法会根据isObserverRead参数来返回一个排序好的MembershipState集合,逻辑就是true就把Observer状态的NameNode放在集合前面,否则就将Active状态的放在前面。接着才是调用远程的msync方法。
if (callStartTime - latestMsyncTime.getValue() > autoMsyncPeriodMs) {
long requestTime = Time.monotonicNow();
invokeMethod(ugi, namenodes, ClientProtocol.class, MSYNC_METHOD, true, new Object[0]);
latestMsyncTime.setValue(requestTime);
}
四、服务端实现
在RPC Server中会判断当前客户端与Active NameNode中的StateId的大小关系:
- 如果C-TXID<N-TXID(NN已经追上),直接由Handler执行
- 如果C-TXID>N-TXID&&NN is far behind,抛出RetriableException由客户端重试(如果Server消费落后的TXID耗费时间会超过客户端连接最长无请求时间)
- 如果C-TXID>N-TXID&&NN is not far behind, reEnQueue 等待NN追上。
Server.Connection#processRpcRequest
if(alignmentContext != null && call.rpcRequest != null &&
(call.rpcRequest instanceof ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcProtobufRequest)) {
// if call.rpcRequest is not RpcProtobufRequest, will skip the following
// step and treat the call as uncoordinated. As currently only certain
// ClientProtocol methods request made through RPC protobuf needs to be
// coordinated.
String methodName;
String protoName;
ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcProtobufRequest req =
(ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcProtobufRequest) call.rpcRequest;
try {
methodName = req.getRequestHeader().getMethodName();
protoName = req.getRequestHeader().getDeclaringClassProtocolName();
if (alignmentContext.isCoordinatedCall(protoName, methodName)) {
call.markCallCoordinated(true);
long stateId;
stateId = alignmentContext.receiveRequestState(
header, getMaxIdleTime());
call.setClientStateId(stateId);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new RpcServerException("Processing RPC request caught ", ioe);
}
}
GlobalStateIdContext#receiveRequestState():判断客户端的State Id与当前NN的State Id
public long receiveRequestState(RpcRequestHeaderProto header,
long clientWaitTime) throws IOException {
if (!header.hasStateId() &&
HAServiceState.OBSERVER.equals(namesystem.getState())) {//客户但没配Observer并且达到obser的时候
throw new StandbyException("Observer Node received request without "
+ "stateId. This mostly likely is because client is not configured "
+ "with " + ObserverReadProxyProvider.class.getSimpleName());
}
long serverStateId = getLastSeenStateId();//通过FSIMage获取最新的TXID
long clientStateId = header.getStateId();
FSNamesystem.LOG.trace("Client State ID= {} and Server State ID= {}",
clientStateId, serverStateId);
if (clientStateId > serverStateId &&
HAServiceState.ACTIVE.equals(namesystem.getState())) {//大于active的时候设置为active的TXID。一般不会出现
FSNamesystem.LOG.warn("The client stateId: {} is greater than "
+ "the server stateId: {} This is unexpected. "
+ "Resetting client stateId to server stateId",
clientStateId, serverStateId);
return serverStateId;
}
if (HAServiceState.OBSERVER.equals(namesystem.getState()) &&
clientStateId - serverStateId >//如果observer的txid落后太多,会抛重试异常由客户端重试
ESTIMATED_TRANSACTIONS_PER_SECOND
* TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toSeconds(clientWaitTime)
* ESTIMATED_SERVER_TIME_MULTIPLIER) {
throw new RetriableException(//根据时间来判断的
"Observer Node is too far behind: serverStateId = "
+ serverStateId + " clientStateId = " + clientStateId);
}
return clientStateId;
Server.Handler#run()
call = callQueue.take(); // pop the queue; maybe blocked here
startTimeNanos = Time.monotonicNowNanos();
if (alignmentContext != null && call.isCallCoordinated() &&
call.getClientStateId() > alignmentContext.getLastSeenStateId()) { //协作的操作可以重新放回call队列中
/*
* The call processing should be postponed until the client call's
* state id is aligned (<=) with the server state id.
// Re-queue the call and continue
*/
requeueCall(call);//重新放到callqueue中
continue;
}
最后用两张图总结: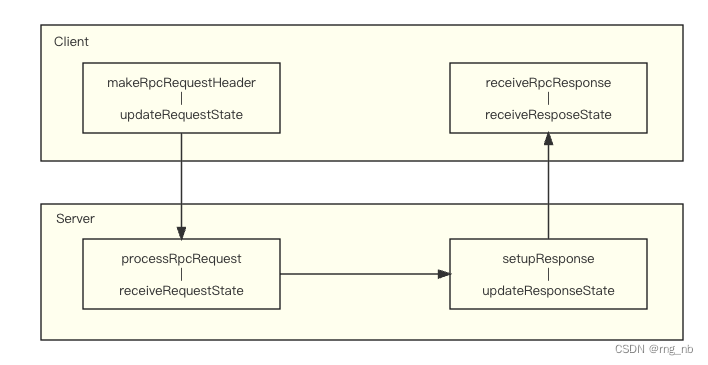
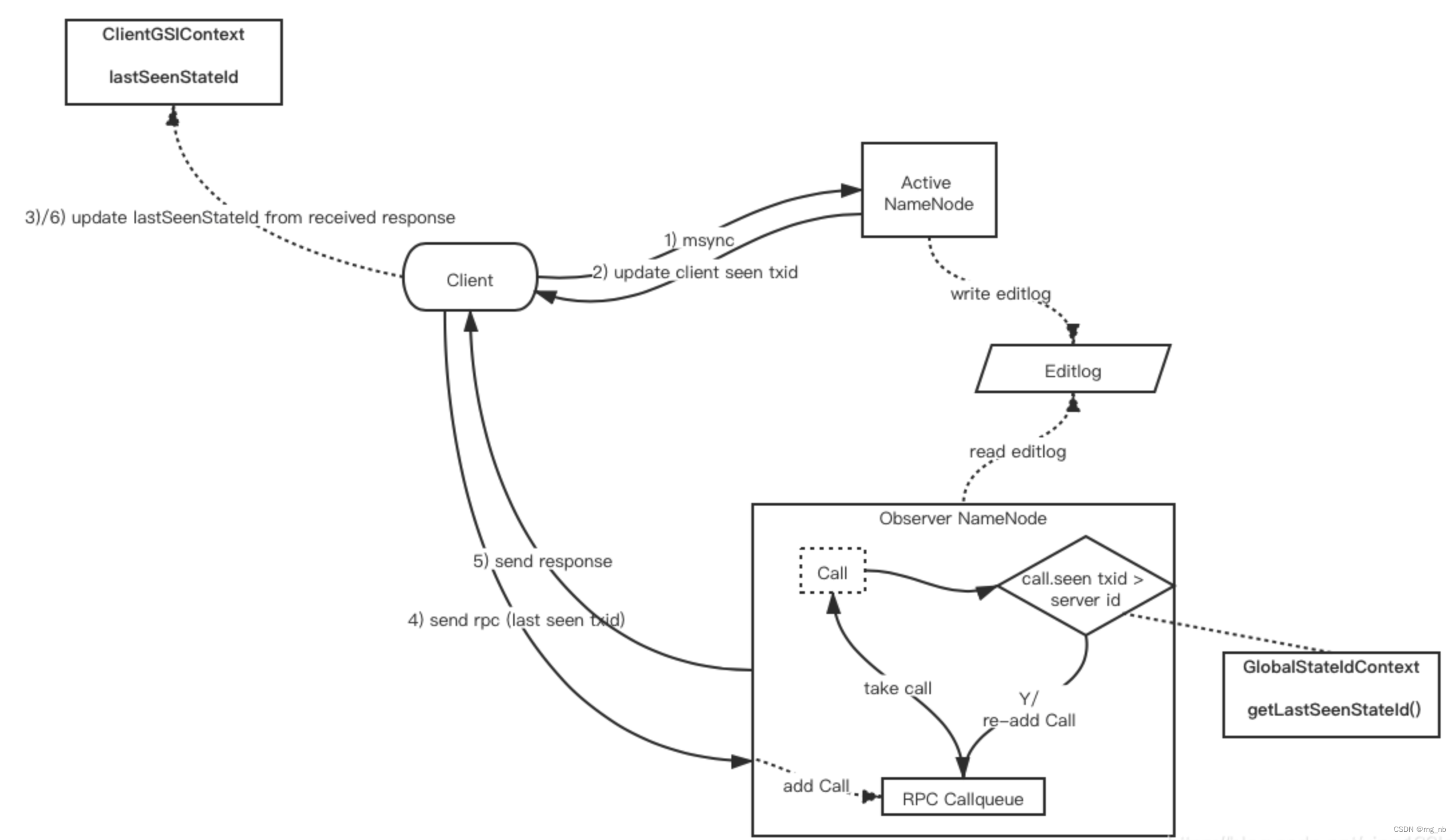
那么在有DFSRouter的情况下,会存在DFSClient,RouterRpcServer,RouterRpcClient交互的情况,AlignmentContext分别使用ClientGSIContext,RouterStateIdContext,GlobalStateIdContext。